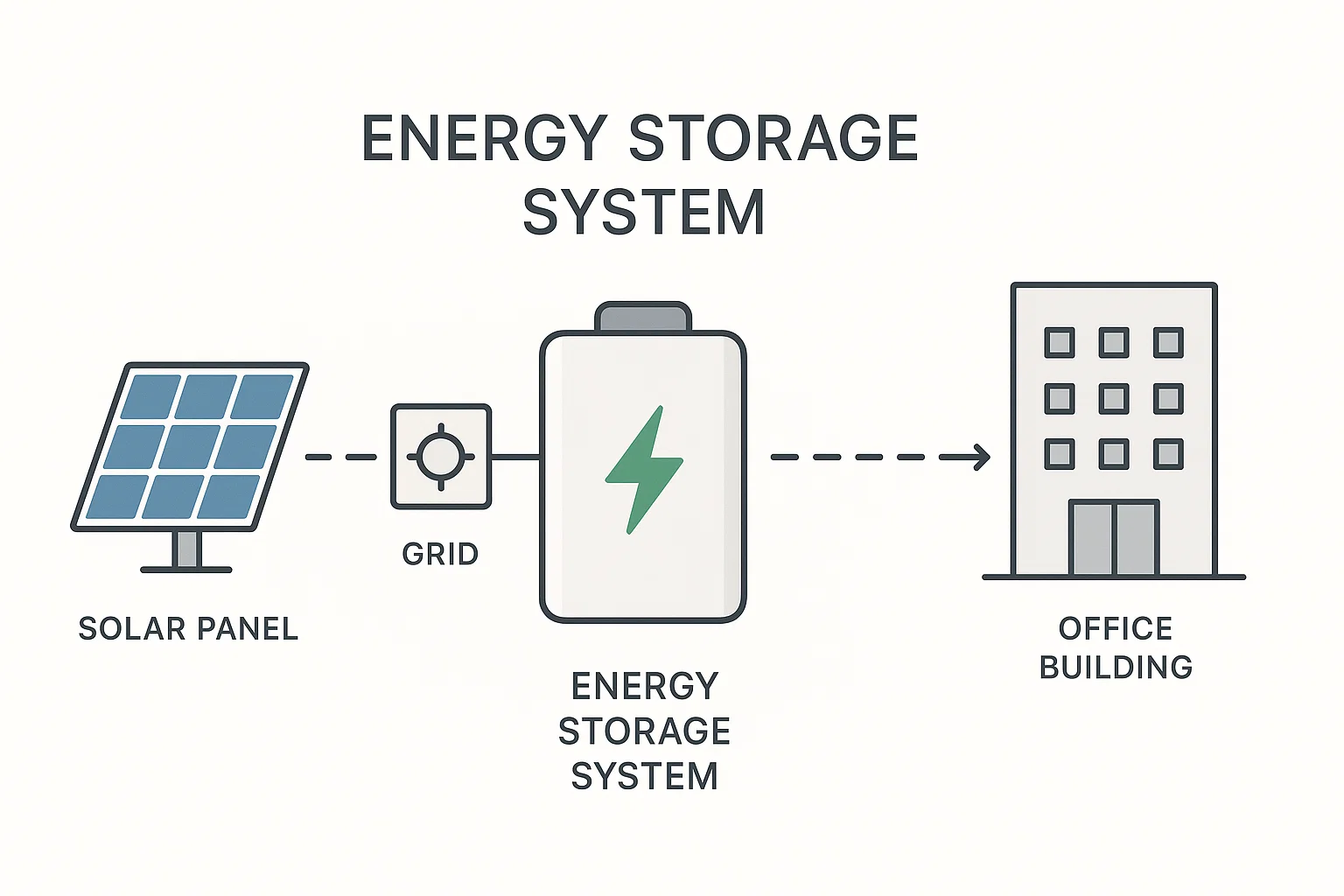
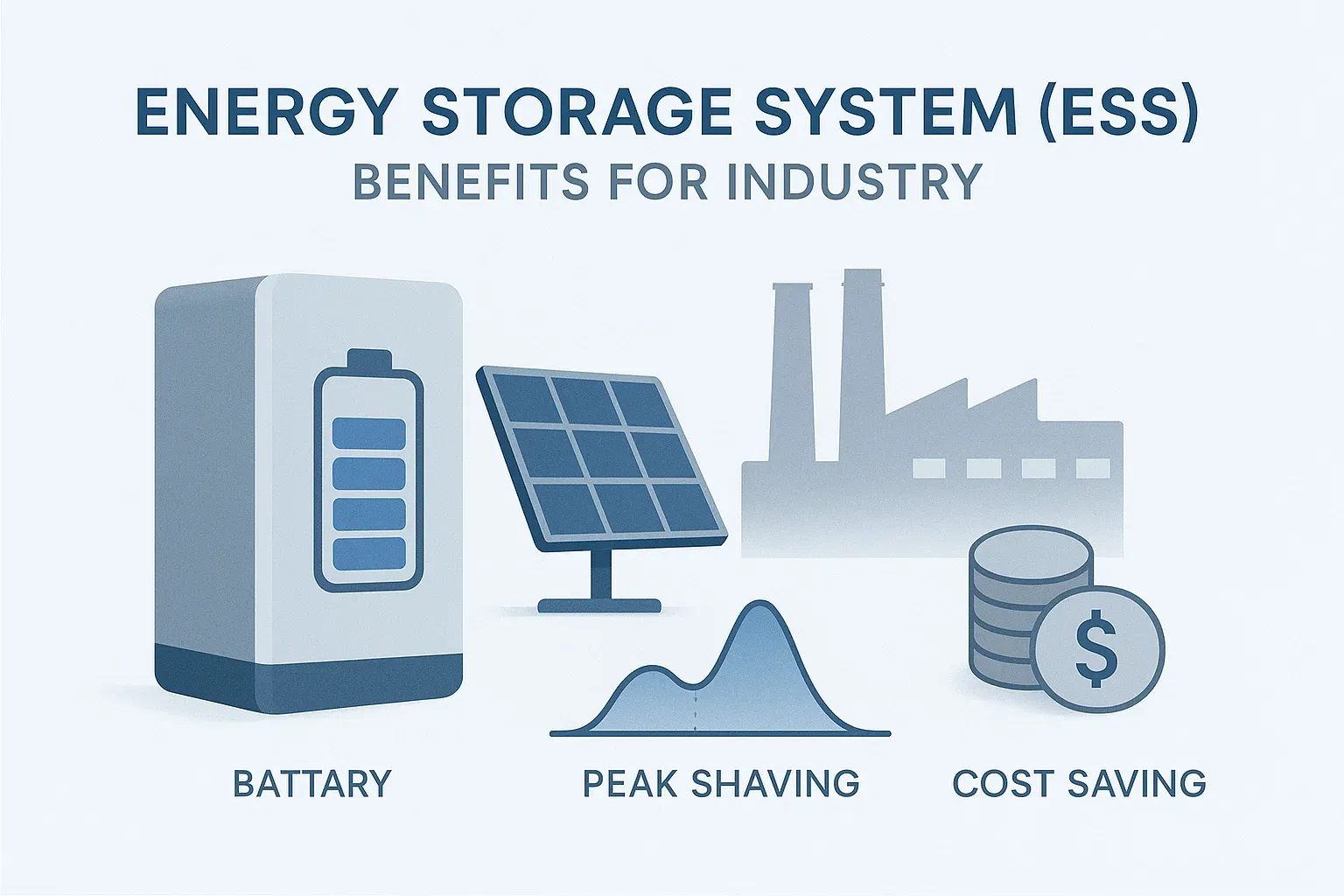
Energy Storage System (ESS) Working Principles Explained: A Guide for Industry Professionals
In today’s dynamic energy landscape, achieving efficiency and reliability is paramount. An Energy Storage System (ESS) is the key, but how does it truly work? This comprehensive guide, designed for engineers and procurement managers, demystifies ESS working principles. We break down the critical components—from the LFP battery system to the PCS, BMS, and EMS—and explain the charge-store-discharge cycle in clear, accessible terms. Discover how to leverage an ESS for peak shaving, renewable integration, and enhanced operational resilience.